Survey & Feedback
Perceptual Mapping 101: Definition, Examples, And How To Make One
Article written by Kate William
Content Marketer at SurveySparrow
12 min read
19 September 2025

60-Second Summary:
Mastering Perceptual Mapping
If you want to truly understand how your brand is perceived and not just what you think it stands for—perceptual mapping is yours to use. It’s a strategic visual tool that maps out how consumers view your brand versus how they view your competitors based on key attributes that matter to them like price, quality, innovation, or trust.
In this blog, you’ll learn:
- What perceptual maps are and why they matter for marketing, branding, and product strategy
- How to build one—from selecting the right variables to plotting your position with real customer insights
- Why it helps uncover market gaps, spot repositioning opportunities, and fuel data-driven decision-making
- Real-world examples that bring the concept to life (and templates to help you get started fast)
Whether you're launching a new product, auditing your brand, or trying to out manoeuver the competition—perceptual mapping will come in handy.
Think about your favourite phone brand. What comes to mind?
Is it the sleek design? The price? The edgy features? Or maybe the user-friendly interface?
Now think about how this brand compares to its competitors. You likely have a mental image of where each brand stands in relation to others on attributes that matter to you.
What you've just done in your mind is exactly what a perceptual mapping aims to capture.
Perceptual mapping is visualization technique that helps businesses understand how consumers view their brand compared to competitors. By plotting these perceptions on a two-dimensional chart, you can gain insights that drive strategic decisions about product development, marketing, and brand positioning.
- What is perception mapping?
- 5 Steps to generate a brand perceptual map from survey data
- Tool to Help with Perceptual Mapping
- Two common types of perceptual mapping
- Benefits of perceptual mapping
- Four perceptual map examples
What is a Perceptual Map? The Definition
A perceptual map is a diagram mapping out what the customers think about your products and services. Aside from just the offerings, it can also map what they think about other brands, even the competitors, and their products.
Finally, perceptual mapping uses customer data to build a viewpoint on where different brands and their products stand within the overall ecosystem.
Since we’re here, it’s also important to mention that a perceptual map isn’t the same as a positioning map. Instead, perceptual mapping measures customer perception, while positioning maps compare the actual traits of a company and its offerings.
Moreover, customer perception might be right or wrong. Great marketing can easily influence it. But positioning maps only capture and compare reality.

Why Does Your Business Need Perceptual Mapping?
Helps find your competitive position - See exactly where your brand stands in audience’s minds compared to competitors
Shows market gaps - Spot the areas that aren't tapped that represent potential opportunities for new products or repositioning
Helps product development - Understand which attributes matter most to consumers so you can improve your offerings accordingly
Informs marketing communications - Helps maintaining the positive perceptions or shift unfavourable ones
Tracks changes over time - Monitor how perceptions changes in response to your marketing efforts and competitor activities
How to Create Perceptual Maps from Survey Data: A Simple 5-Step Process
It’s a ‘Perceptual Map 101’ article, and how can we not talk about the process of building such a map? So let’s give you the steps to create a perceptual map understood by all. This is where the fun part begins!
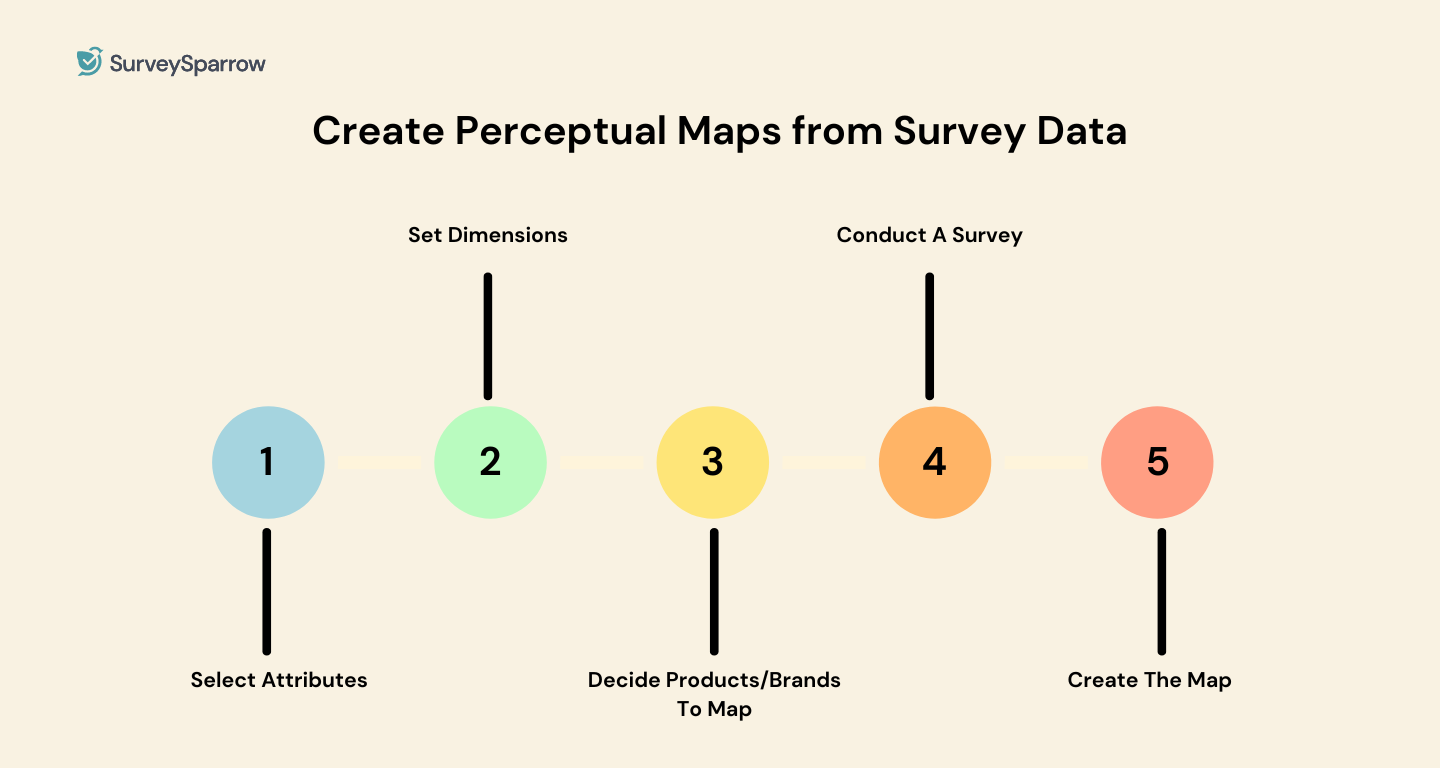
Step 1: Define the Scope and Select Attributes
Selecting attributes is the first and probably the most integral step for any perceptual map. Attributes that matter to your target audience gives these maps a real meaning. The target audience and customers use these attributes to compare your products with the competitors.
Their perceptions might not be highly logical, but remember, this is a perceptual map, not positioning, so their thinking matters the most. Depending on the purpose of your map, these attributes change, and it’s always good to use those that are important from an average customer’s point of view, as they cover a wide range of your target market.
Common attribute pairs include:
Price vs. Quality
Traditional vs. Innovative
Practical vs. Luxurious
Simple vs. Feature-rich
For example, if you want to develop a perceptual map for a camera, the lens quality, zoom, ease of use, or total memory could be the prime attributes. Similarly, for shoes, it could be comfort, design, or durability, out of which you could select any two.
Step 2: Set Dimensions
After attributes, this is the most crucial step to perform. Setting dimensions for your map allows the customer’s perceptions to be reflected clearly. This process involves giving numerical values on each axis. More numerical values will cause better mapping.
So, if you’re mapping the axis in twos, the result will be more precise compared to when you map it in fives. Setting the correct dimensions, thus, is crucial for perceptual maps to reveal more accurate information.
Step 3: Decide Products/Brands To Map
If you want to build a perceptual map for shoes, different shoes from different brands or varying styles need to be selected. These brands can be your competitors or a part of your product umbrella.
This step is crucial to increase the efficiency of your map, as when you choose the right products, customer perceptions from the map can lead to needed changes. That’s the end goal, right? To continuously improve and grow?
Step 4: Conduct A Survey
Perceptual maps thrive on data, and conducting surveys to understand brand perception are the best way to do that. The survey building process is as simple as it can get with SurveySparrow, which allows you to get to the analysis and actual mapping stage faster.
The questions, however, should be asked in this manner:
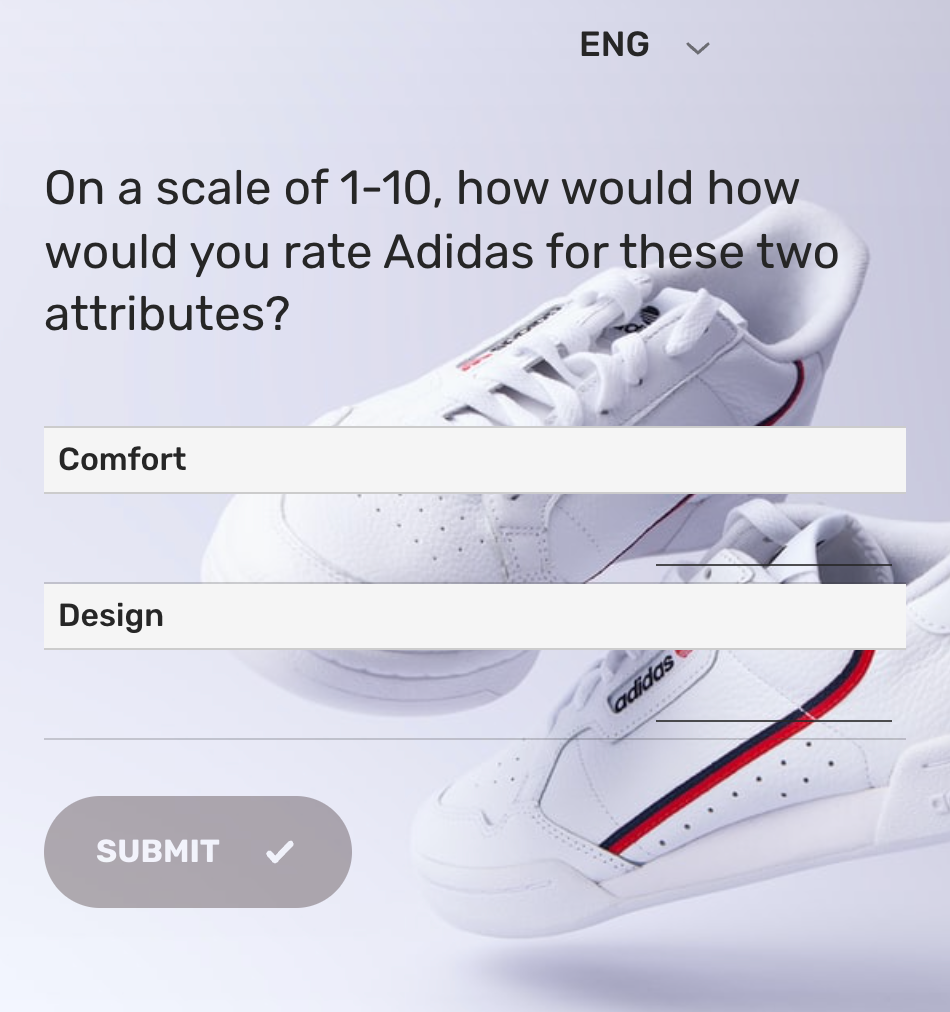
The question structure is repeated for all products and brands, and in the end, you’ll get a scale value for each shoe and its brand for comfort and design. Of course, the scale value will alter based on your set dimensions.
See, open-ended questions can also be used here, but they won’t have straightforward answers as we’ll get here. So, it’s best to stick to such scale-type questions for perceptual maps.
SurveySparrow has all the tools you need to create accurate perceptual. You can sign up below to try all of our features for free.
14-day free trial • Cancel Anytime • No Credit Card Required • No Strings Attached
Step 5: Create The Map
Once you’ve scored the brands using their products or directly the brand, it’s time to build your perceptual map and plot the results. This is the easiest step of the process and is similar to how we plotted line graphs in schools.
The X-axis represents one of the selected attributes with the pre-fixed dimensions, and the Y-axis represents the other attribute with its dimensions. Plot it, and you’ll get a clear picture of the customer’s perception of a specific product category.
Tool that Helps with Perceptual Mapping
If you are looking into identifying what’s working best (or worst) for your business, then SurveySparrow can help you with it.
SurveySparrow uses advanced NLP and statistical techniques to make sense of your customer (unstructured) data. These are usually open-ended questions that are difficult to analyze – not for SurveySparrow.
You can eliminate the guesswork out of the game and look into specific areas in your business. The following is an example of how SurveySparrow uses perceptual mapping in its key driver analysis.
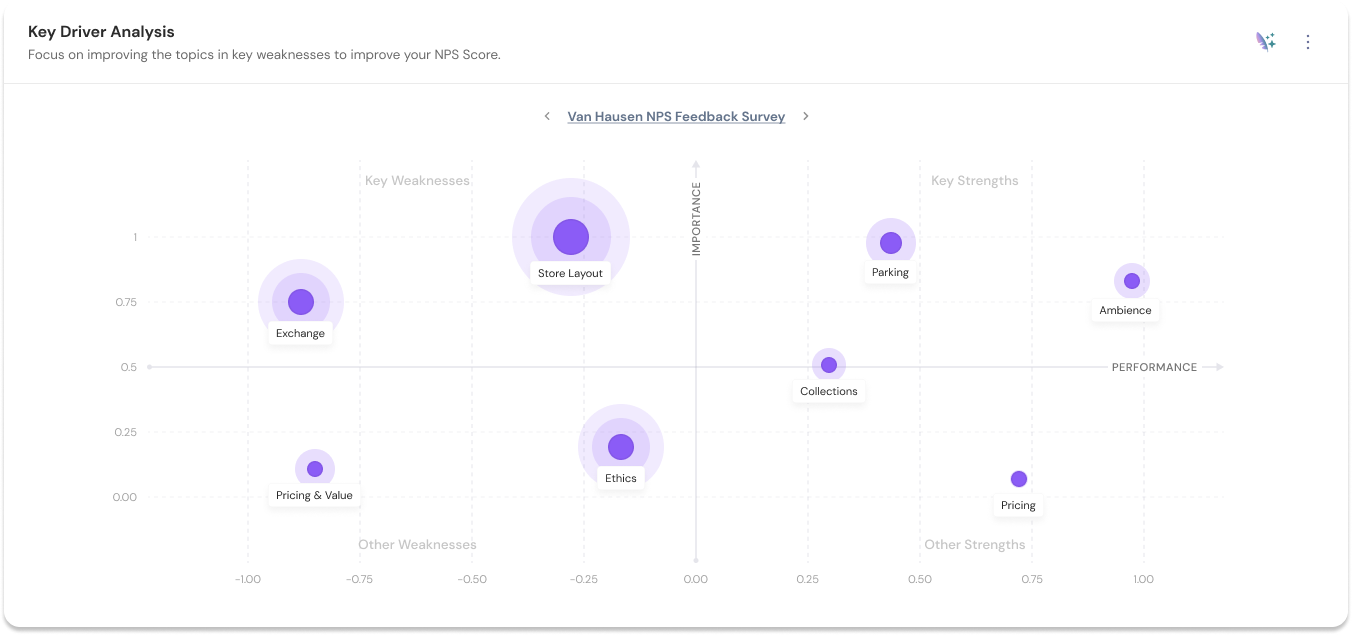
As you can see from the image, the tool will clearly depict your business’s strengths and weaknesses in a perceptual map. This allows for a quick understanding of what’s working best for you and worst for you.

2 Common Types Of Perceptual Maps
There can be 2 types of perceptual maps: the standard and the multi-dimensional. Their usage depends on the case at hand, and since we’ve discussed perceptual maps so well, why leave this? Let’s look at both types.
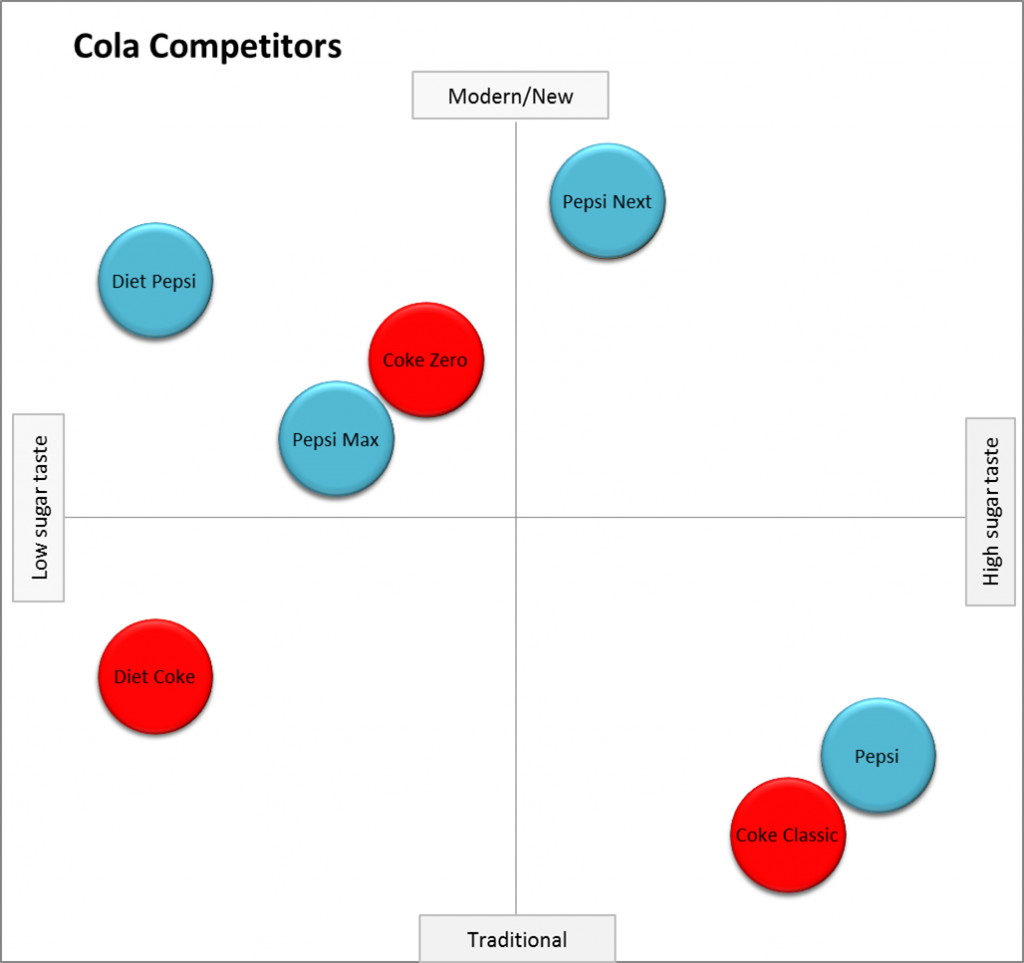
1. Standard Perceptual Map
The standard perceptual map has two-axis and visualizes collected data to communicate key findings. In other words, a standard perceptual map highlights the key findings from a survey quickly with minimum hassle.
2. Multi-Dimensional Scaled Perceptual Map
A multi-dimensional scaled perceptual map is used to present an overall analysis of the marketplace. It provides additional insight using statistical tools like the Excel template. Plus, it requires an expert who can map and interpret correctly to reveal essential information. For large-scale research purposes, this perceptual map type is used.
Some Benefits Of Using A Perceptual Map
You know all about perceptual maps, but one aspect. What’s that? The benefits. And there are many, of which some you know and some you don’t. So, here are the top benefits of using a perceptual map:
- You accurately know the opinions of your customer base. How powerful is that!
- With perceptual maps, you don’t just know their opinions but also understand how vital the selected attributes are for the customers.
- You have a good idea of what your competition is doing better than you.
- Is the target audience resonating with your brand’s identity? You get to know that accurately using a perceptual map.
- Identifying market gaps becomes easy, as the map does that for you.
- Changes to marketing and sales strategies are made after findings from these maps that lead to better campaigns and more conversions.
- With your customer’s perception of 2 different attributes on the map, you get to see how the ecosystem of your industry is evolving and how to reposition the company in it.
4 Simple Perceptual Map Examples
We’ve given the definition. Now, let’s see some examples where perceptual maps are commonly used.
Perceptual mapping does a great job of finding customer perspectives for two unique attributes. But where are these maps used, and why?
1. New Product Launch
Perceptual maps help managers identify market space where new products can be launched. How? They analyze gaps in the map where it’s clear the target market isn’t satisfied with the current line of products.
As you’ll see, these gaps will determine the degree to which a new product successfully satisfies the two chosen attributes. Identifying features that aren’t working also becomes clear while analyzing perceptual maps.
The best part? As a decision-maker, you’re seeing everything from the eyes of the customer. So, if they like a specific feature of your competitor’s product, you’ll know it from the map, which will then allow you to improve yours. So, perceptual mapping provides evidence for launching a new product or bringing the needed changes.
2. Marketing Campaigns
This is where perceptual maps are used the most. Online or offline marketing campaigns work best when your team understands what customers like and dislike. That’s why terms like ‘perceptual map marketing’ are gaining popularity
Customer perception weighs in gold for any marketing team. So, marketers get to know what customers are thinking about both your and your competitor’s products. This helps bring more effectiveness to their campaigns, improving the chances of success.
Even finding the most liked campaign becomes easy with perceptual maps. Of course, the quality of collected data should be high for these maps to tell the right story, but look at the ROI it’s giving to the marketing team.
3. Improving Customer Engagement
Your customer support team also needs support! We often forget that and focus on other business vertices, but your support team also needs to know where customers engage when they’re online? What type of support are they liking? And what’s there to improve?
These questions are answered using the correct variables with perceptual maps. And when the nature of customer engagement is explicit, the support team can make changes to attain customer satisfaction and make them loyal followers of your brand.
Sales!
Perceptual maps play a pivotal role for your sales team by narrowing down the most critical variables for the target market. This helps representatives talk in a focused way, addressing the pain points during sales calls.
Perceptual region maps also allow managers to develop strategies that can bring more sales. They focus on what matters to the target group rather than focusing on what matters to them. A tremendous shift in mentality and a perceptual map is very much the reason.
4. Determining Brand Identity
“What do our customers think about our brand? What’s our identity in their minds?”
If that’s your question, conduct customer surveys by selecting 2 identities representing the brand correctly and mapping the findings. A perceptual map is the best way to determine if the customers have the proper brand identity in mind. If not, steps can be taken to correct that quickly.
Winding Up
Now, we can say that we’ve covered everything about perceptual maps here. And there’s one thing we saw. Perceptual maps require good data.
Yes, when the data collected from customers is excellent, the perceptual map will turn out great. It’s that simple.
This is where we come in. We handle the first part so that you can focus on the second. Our customer feedback surveys, coupled with chatbot support and various questions, let you correctly collect information. So check everything out, and if you need us with anything, we’re here.
So, make the right decision, collect the right data, and build the perfect map. We’re rooting for you!

Create engaging surveys that people actually complete. Try SurveySparrow now!
Kate William
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Most effective perceptual maps include between 5-10 brands or products. Including too few limits competitive insights, while too many makes the map cluttered and difficult to interpret.
For fast-moving industries, updating your maps quarterly is advisable. For more stable industries, annual updates may be sufficient. Additionally, consider creating new maps after major product launches or marketing campaigns.
While often used interchangeably, perceptual mapping specifically refers to how consumers perceive brands, while positioning mapping can also include where companies intend to position themselves.
Yes! SurveySparrow's intuitive survey platform makes it easy to collect the consumer perception data needed for creating accurate perceptual maps. Our analytics features also help you interpret the results effectively.
Related Articles

Survey & Feedback
Top 8 Survey Incentives to Increase Response Rates
15 MINUTES
8 July 2021

Survey & Feedback
15 Best Medallia Competitors & Alternatives of 2024
23 MINUTES
16 June 2022

Survey & Feedback
How to Write a Perfect Customer Feedback Survey Invitation?
7 MINUTES
28 January 2026

Survey & Feedback
Why Should You Use An Online Survey Software In 2024
14 MINUTES
27 January 2021
