Customer Experience
How to Create a Retail Customer Journey Map
Article written by Parvathi Vijayamohan
Content marketer at SurveySparrow.
9 min read
19 September 2025

Ever wondered why shoppers abandon their carts (or your brand) ?
The answer often lies in a journey you haven’t fully mapped yet.
This blog explores how building a retail customer journey map can transform how you understand and optimize the entire buying experience.
Here’s what you’ll learn:
- What a retail customer journey map really is and why it’s more than just a diagram.
- The 5 critical stages of a shopper’s experience—Awareness, Consideration, Purchase, Retention, and Advocacy.
- How mapping each touchpoint (in-store, digital, mobile, support, etc.) uncovers hidden friction that may be costing you sales.
- Common pitfalls retailers make—like neglecting the post-purchase experience or failing to unify online and offline channels.
- Real-world benefits: Personalization that actually works, higher conversion rates, reduced churn, and better brand loyalty.
- A simple, step-by-step framework to start mapping your own customer journey—complete with tools, templates, and examples.
If you’re in retail, you’ve probably heard the phrase “walk a mile in your customer’s shoes”. Well, a retail customer journey map can help you walk that mile in minutes.
In this blog, we’re going to take you through:
- The retail journey map: In a nutshell
- How to create a retail journey map in six steps
- A (fictional) example of a retail customer journey map
What is a retail customer journey map?
Why does Dave load his cart with his wishlist items only to close the tab?
Why does Feifei spend hours shopping for that one specific product only to put it back on the shelf?
Also, why do users download your app only to uninstall it after just one session?
Retail customer journey mapping can help you find the answers.
A retail journey map is a visual representation of the customer’s journey. Shown in a map, timeline or flow chart format, it gives a quick visual breakdown of your business through the customer’s POV.
From the beginning till the end and post-purchase, retail customer journey maps walk you through the different stages of the consumer’s experience with a retailer. Typically, a retail journey map includes three stages: pre-purchase, purchase, and post-purchase. So retail customer journey mapping is the process of mapping out these stages and the key touchpoints within each stage.
The average cart abandonment rate across all industries is 69.57%, according to Drip.com.
Ready to map your retail customer journey? With SurveySparrow‘s executive dashboards, you can create appealing visual retail journey maps that you can share as a password-protected file or download as a PDF.
Sign up for free to try it out.

Explore Deeper Customer Insights with SurveySparrow
A personalized walkthrough by our experts. No strings attached!
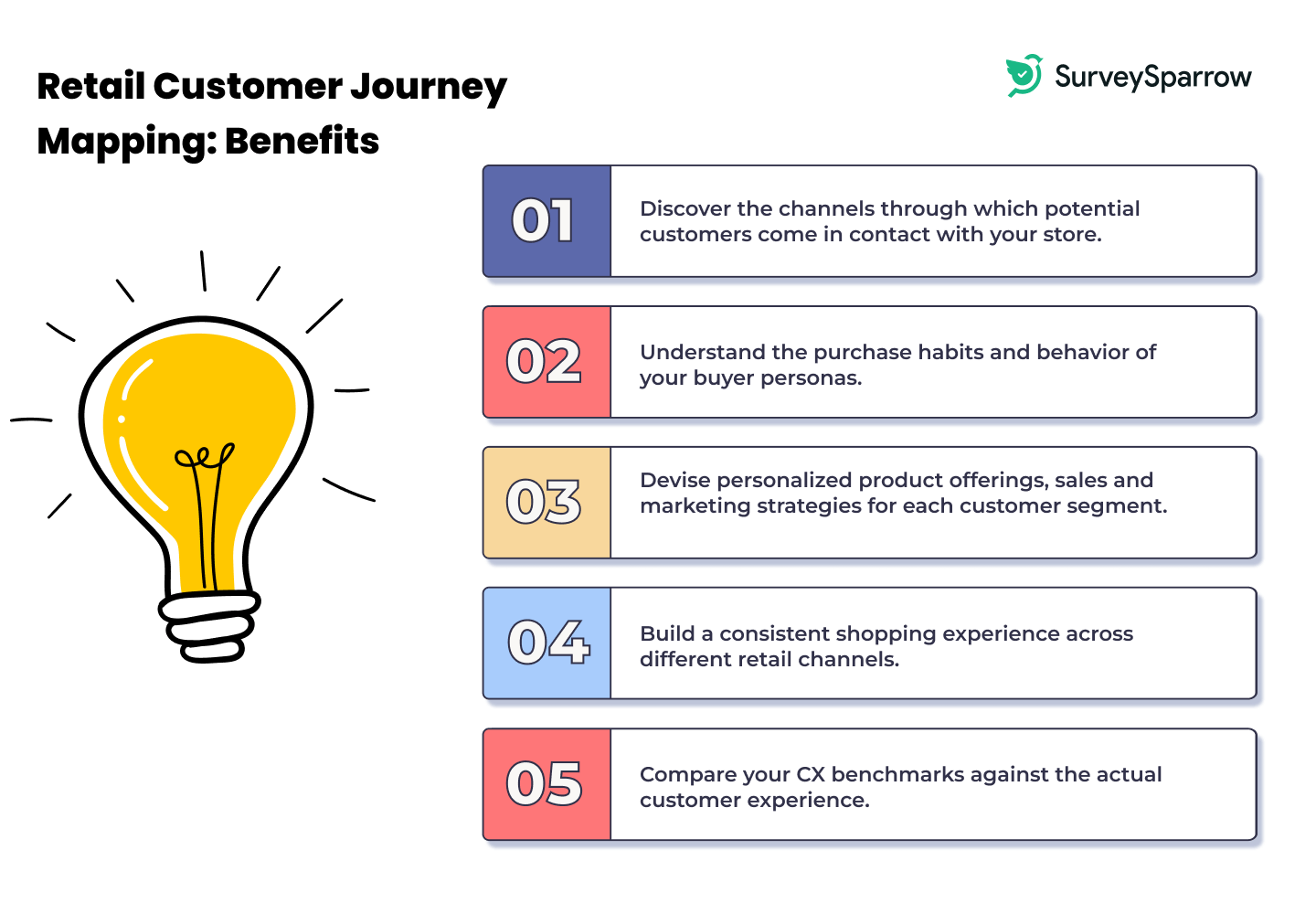
Why is a retail customer journey map important?
A retail customer journey map is important for a lot of reasons
- Understanding the Customer Experience: It helps retailers understand the various stages customers go through when interacting with their brands. This includes pre-purchase, purchase, and post-purchase phases, providing insight into customer needs and behaviors at each stage.
- Identifying Pain Points: By mapping the customer journey, retailers can identify specific pain points or challenges customers face. This understanding allows for targeted solutions to improve the overall customer experience.
- Enhancing Customer Engagement: A journey map can highlight opportunities for enhancing customer engagement and personalization. Retailers can tailor their interactions based on the preferences and behaviors of customers at different journey stages.
- Driving Sales and Loyalty: By optimizing the customer journey, retailers can improve customer satisfaction, increasing sales and customer loyalty. A positive experience often results in repeat business and referrals.
- Strategic Decision Making: Customer journey maps provide valuable data that can inform strategic decisions, such as where to allocate resources, how to develop marketing strategies, and which areas of the customer experience need improvement.
- Cross-Channel Consistency: In the multi-channel retail environment, journey mapping ensures consistency across all customer touchpoints, whether in-store, online, or mobile platforms, creating a seamless and integrated experience.
- Feedback and Continuous Improvement: It serves as a tool for collecting customer feedback and monitoring changes in customer behavior, allowing for continuous improvement of the retail experience.
How to create a retail customer journey map
Here are the six basic steps to follow in order to create an accurate retail customer journey map for your business.
Step #1: Fix a goal
Define the overall goal of your retail customer journey mapping project. This will help you determine which customer actions to track and analyze.
Moreover, depending on the size and scope of your retail operation, the goals may range from increasing online sales to improving in-store experiences.
Step #2: Select your tracking tools
The second step is deciding how to track and measure customer journeys.
This can include tracking customer behaviors through website analytics, surveying customers directly, or using social media platforms to observe trends and conversations around retail products and services.
Step #3: Gather data
Next, we gather the data associated with each retail customer journey stage. This data can be collected through a variety of sources, such as website analytics, surveys, or interviews.
In order to gain an accurate picture of the retail customer journey, it’s important to collect data from all stages.
Step #4: Plot the touchpoints
The third step is to identify the touchpoints in the retail customer journey. If you want to create a truly omnichannel retail experience, you have to enable the customer to transition between multiple touchpoints smoothly.
To map out your touchpoints, you can break down your stages further into specific customer actions. These can be actions such as browsing online reviews, clicking on an ad, visiting a store location, creating an account, or contacting customer service.
Step #5: Flesh out the map
The fifth step is to analyze the available data and expand on your retail journey map. This involves looking for patterns and trends as well as identifying any potential areas of improvement.
Once it’s plotted out, the retail customer journey map can inform decisions on optimizing the customer experience.
Step #6: Update the map
Finally, it’s essential to regularly review and update the retail customer journey map as new data is collected over time.
This will help ensure that your retail business remains up-to-date on consumer behaviors and preferences, allowing for better user experience optimization.
5 Best retail customer journey map examples
1. Amazon
We all know Amazon as the world’s largest internet retailer.
But, as this map of Amazon shows, it is also jungle-like in the scale of its ecosystem, with subsidiaries and verticals that include:
- AI
- Groceries
- Books
- Live streaming
- Healthcare
- Digital content services, and more. Phew!
To keep things simple, here’s a basic, imaginary example of what a retail customer journey map would look like for Amazon’s online shopping app.
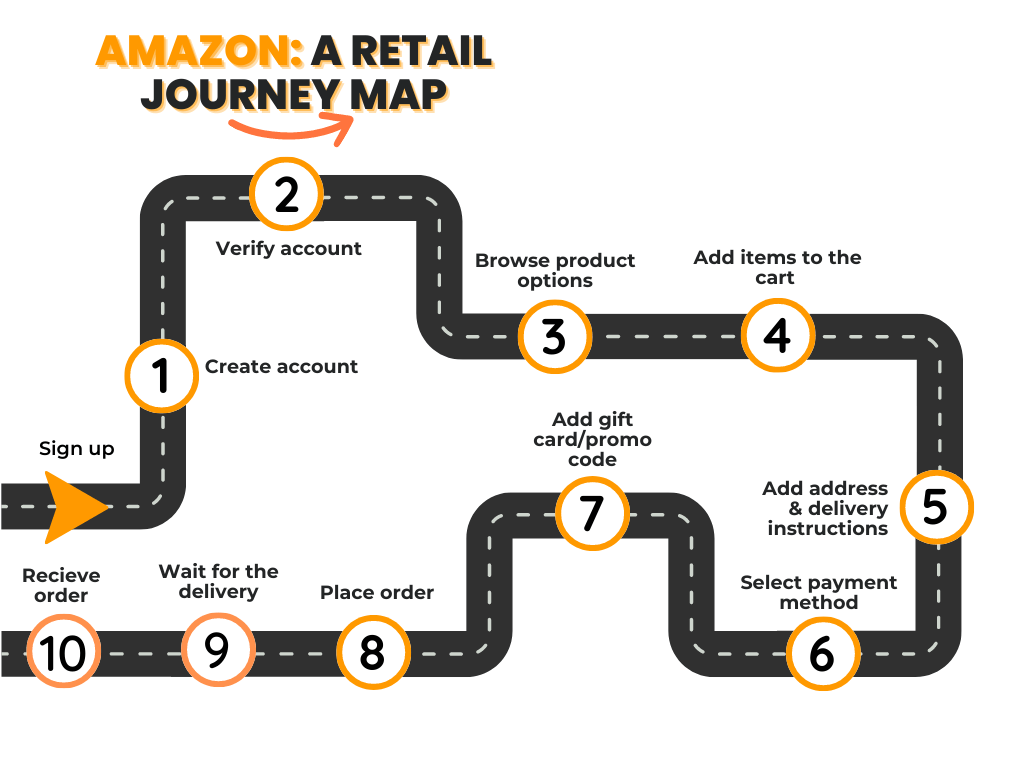
Now, let’s break down the touchpoints, aka customer actions, by the three basic stages.
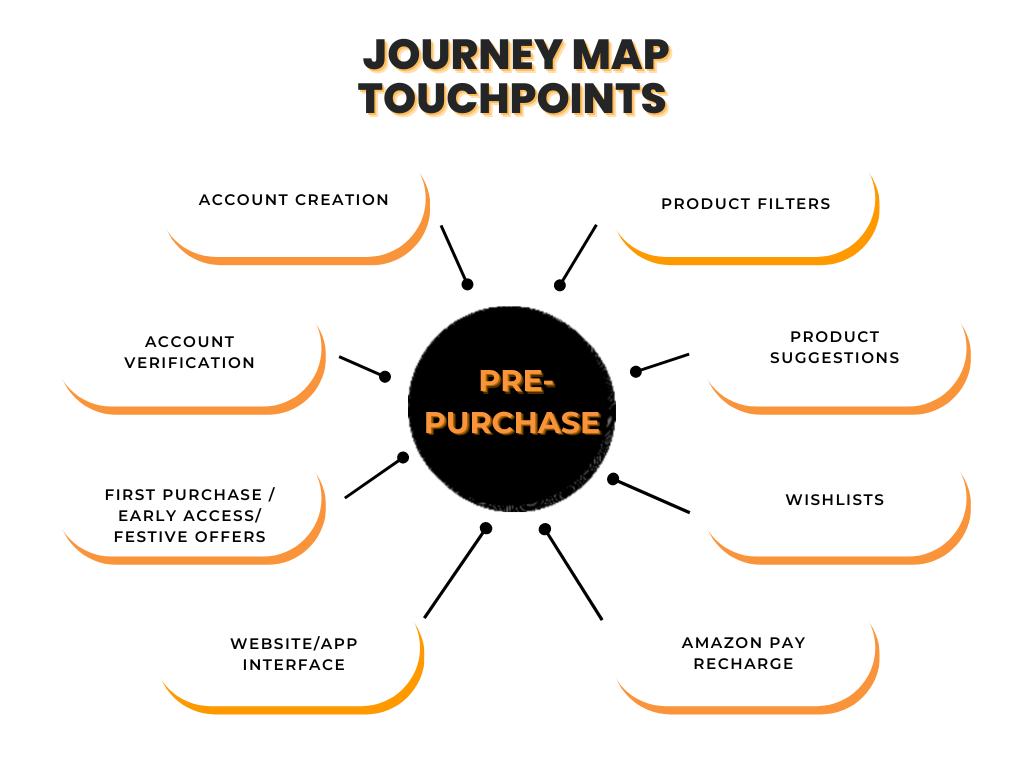
For the above stage, we can collect data from sign-up forms, site/app analytics, CSAT, and CES surveys.
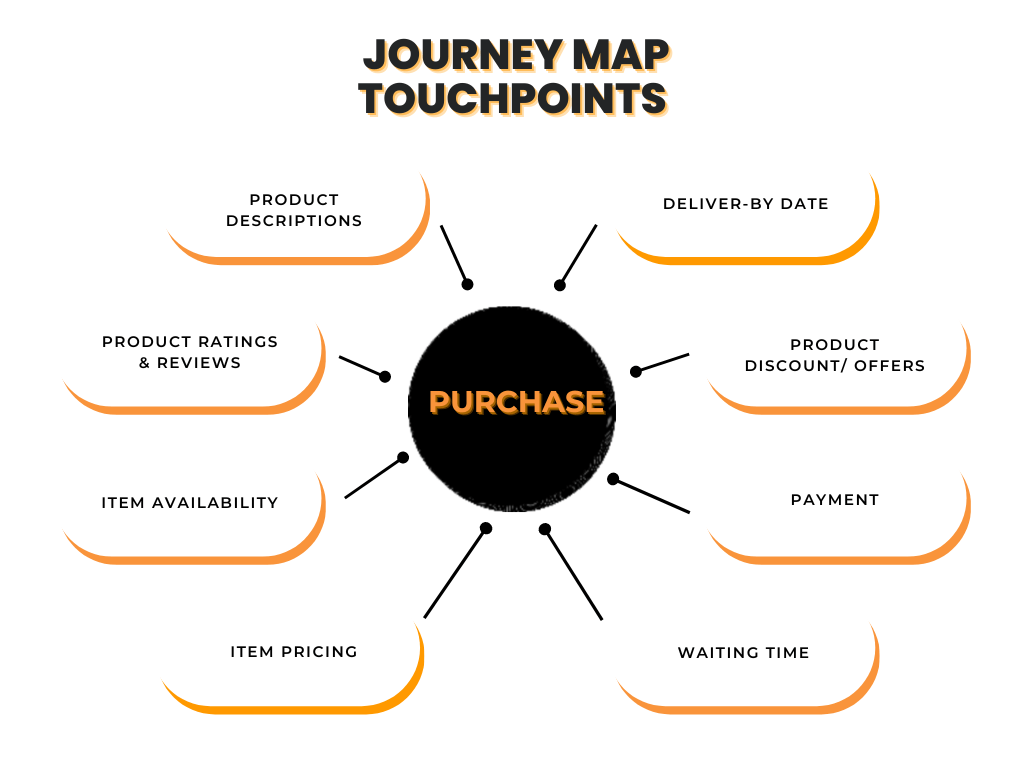
In the above phase, it’s crucial to use analytics to monitor abandonment. Additionally, timely reminders, hassle-free checkout forms, flexible delivery options, and a guest checkout option can help craft a smoother shopping experience.
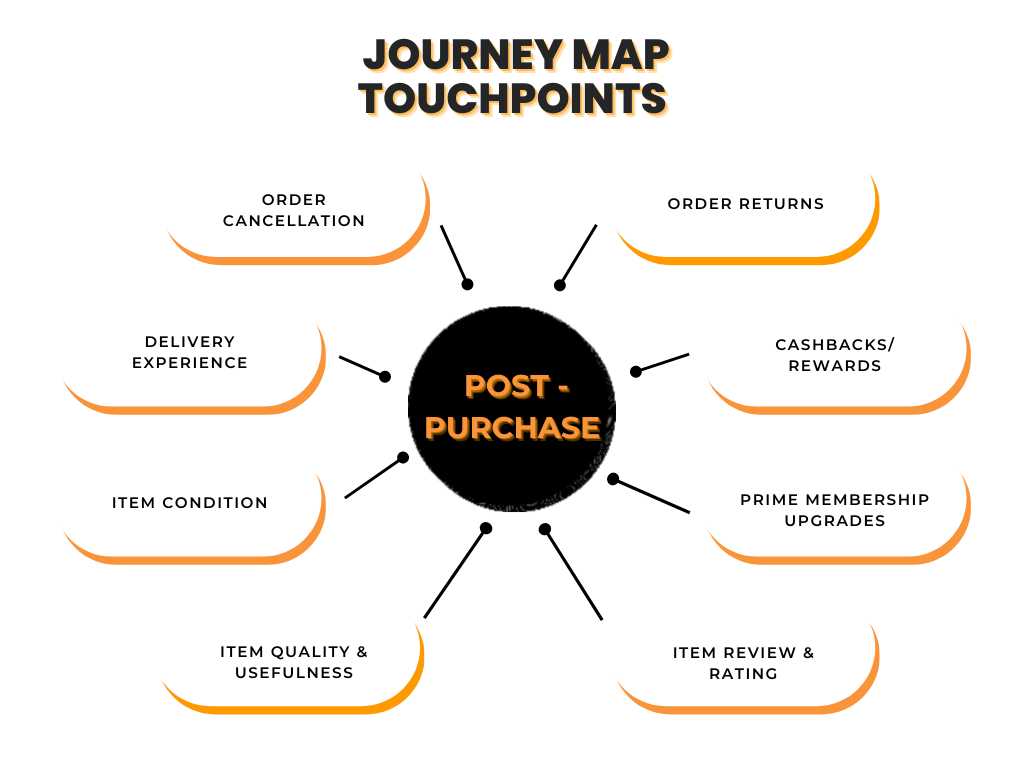
In this phase, we can use the following tools to get data on the touchpoints above:
- NPS surveys
- Rating scale surveys
- Multiple-choice forms
- Qualitative feedback in the form of reviews, etc.
Enhance Your Business with Authentic Feedback: Discover the Power of Targeted Surveys to Unlock Actionable Insights.
Sign up for free!
14-day free trial • Cancel Anytime • No Credit Card Required • No Strings Attached
2. Apple Store
Discovery: Customers often learn about new Apple products through online ads, social media, or word of mouth.
Consideration: They visit an Apple Store to experience the products hands-on, benefiting from the minimalist store design and product-focused displays.
Purchase: Customers receive personalized assistance from Apple’s staff (known as ‘Geniuses’) who help with product selection and offer a seamless checkout process.
Post-Purchase: Apple follows up with setup assistance, invites to workshops, and offers support through the Genius Bar.
Loyalty: Customers often become repeat buyers due to the quality of products and customer service, and may also engage with the brand through its iOS ecosystem and online services.
3. Nike
Awareness: Their marketing campaigns, athlete endorsements, and product innovations draw customers to Nike stores.
Engagement: In-store, customers can try on products, often with the assistance of knowledgeable staff. Nike stores frequently feature engaging, dynamic displays and even areas for product testing.
Purchase: The purchase process is enhanced by Nike’s integration of technology, like mobile checkout options.
Post-Purchase: Nike encourages customers to join their NikePlus membership for additional benefits, and often follows up with personalized marketing.
Loyalty: Through their membership program, Nike keeps customers engaged with exclusive product releases and tailored recommendations.
4. IKEA
Planning: Customers often start their journey by browsing the IKEA catalog or website.
Store Visit: The IKEA store experience is unique, with a carefully designed showroom path leading customers through various home setups and inspiring purchases.
Purchase: Customers select and pick up flat-packed products from the warehouse section and proceed to checkout.
Assembly and Use: After purchase, customers assemble the products at home, an integral part of the IKEA experience.
Follow-up: IKEA follows up with emails, offering additional products, tips for home improvement, and customer support.
5. Sephora
Discovery: Customers often learn about new beauty products through Sephora’s extensive online and social media presence.
In-Store Experience: In-store, customers can try samples, get a makeup consultation, and attend beauty workshops.
Purchase: Sephora offers a seamless purchase process with helpful staff and a loyalty program (Beauty Insider) that provides rewards and personalized recommendations.
Post-Purchase: Customers receive follow-up emails with beauty tips, product recommendations, and information on upcoming sales.
Loyalty: Sephora’s loyalty program keeps customers engaged with exclusive offers, special events, and early access to new products
Wrapping Up
We hope the pointers above will help you create your customer journey map. Aside from building a truly omnichannel experience, such a tool can also help you ensure that you meet your customer’s needs.
For example, if you’ve noticed that customers prefer to talk to customer service before making a purchase, you can set up a chatbot to answer frequently asked questions. If your audience is active on social media, you can use a reputation management tool to monitor negative reviews.
Happy surveying!

Make your customers feel heard. Turn feedback into loyalty with SurveySparrow's CX platform.
Parvathi Vijayamohan
Parvathi is a sociologist turned marketer. After 6 years as a copywriter, she pivoted to B2B, diving into growth marketing for SaaS. Now she uses content and conversion optimization to fuel growth - focusing on CX, reputation management and feedback methodology for businesses.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Retail journeys are often more multi-channel. Unlike SaaS or services, retail has to consider both physical and digital touchpoints. That makes mapping these journeys even more important — and more complex.
Every 6 to 12 months is a good rhythm — or anytime there’s a major change (new product, new channel, rebrand, etc.). Customer behavior evolves quickly, especially in retail, so it’s not a one-and-done exercise.
Yes! That’s one of the most overlooked benefits.
A retail customer journey map can show where people hesitate in-store, where staff interactions can improve, or how digital signage and layout affect behavior.
Related Articles

Survey
50+ Retail Survey Questions to Ask Your Customers for Feedback
12 MINUTES
19 September 2022

CX
How to Create a Retail Customer Journey Map
9 MINUTES
15 December 2022

NPS
NPS in Retail (2025): Benchmarks, Case Studies & 7 Proven Ways to Lift Loyalty
11 MINUTES
27 February 2024

Customer Experience
Top 5 Customer Service Trends for 2026
11 MINUTES
31 December 2020
