Survey & Feedback
Design Research: Types, Methods, and Importance
Article written by Kate Williams
Content Marketer at SurveySparrow
8 min read
19 September 2025

What do you think is the first recorded design research? Does it date back to the Renaissance? If so, was it when the artists of the age meticulously studied human anatomy to craft sculptures? Intriguing right?
Design research is more than just a process. It is what shapes everything that we come in contact with. This blog will look into its meaning, importance, and all that you need to know.
What is Design Research?
Design research is the systematic investigation that fuels innovation by understanding user needs, preferences, and behaviors. Through methods like surveys and usability testing, it uncovers valuable insights, guiding the creation of user-friendly products. This research-driven approach ensures designs are visually appealing but also functional and intuitive, aligning seamlessly with user expectations.
From shaping everyday gadgets to revolutionizing user interfaces, it forms the foundation for impactful and user-centric design solutions. Let’s take the iPhone for example. Have you ever wondered why they are so easy to use? That’s because the makers studied how people use phones, allowing them to design a device that everyone finds simple and enjoyable.
Types of Design Research
Design research bridges the gap between creativity and practicality. It transforms concepts into tangible, user-friendly solutions. There are many specialized branches and let’s take a look at them:

1. Exploratory Research
This is the preliminary phase of the research process. It employs qualitative methods such as interviews, focus groups, and ethnographic studies. Researchers aim to understand user behaviors, motivations, and preferences without predetermined hypotheses. The data collected is qualitative and lays the foundation for further investigation.
Let’s say, you are a software development company planning to create a new project management tool. In the exploratory research phase, researchers conduct in-depth interviews and focus group discussions with potential users. They aim to understand users’ current challenges in project management, their preferences for features, and their preferred user interfaces.
2. Evaluative Research
Suppose an e-commerce website wants to evaluate the usability of its checkout process. In evaluative research, usability testing can be conducted. (If you’re confused, these Website Usability Survey Questions might help you!)
Participants are given specific tasks, such as adding items to the cart, applying a discount code, and completing the purchase. Researchers observe participants’ interactions and collect quantitative data, like task completion rates and error occurrences.
They evaluate the usability, functionality, and effectiveness of a product based on specific criteria. By analyzing this data, the website identifies usability problems, such as confusing button placements or unclear instructions, and makes necessary improvements for a smoother user experience.
3. Generative Research
Generative research is the creative phase aimed at generating new ideas and concepts. It employs qualitative techniques like brainstorming sessions, ideation workshops, and participatory design activities. Researchers facilitate collaborative sessions with multidisciplinary teams and end-users to explore innovative solutions.
Through collaborative brainstorming activities, such as mind mapping and sketching, participants generate creative ideas. These ideas might include unique interaction gestures, novel content-sharing methods, or innovative community-building features. The best part? It fuels creativity!
4. Usability Testing
Here, researchers observe participants’ interactions, measuring metrics such as task completion time and error rates. If users struggle to find the appointment scheduling feature or encounter confusing navigation, the organization can identify these issues and redesign the interface for a more intuitive and efficient user experience.
Participants are given specific tasks to perform, and their interactions are recorded and analyzed. It employs controlled experiments and quantitative metrics, such as task completion time and error rates.
5. A/B Testing
A/B testing, also known as split testing, compares two versions of a design to determine which performs better. Variations in design elements, such as colors, layouts, or call-to-action buttons, are tested on real users. By analyzing user interactions and conversion rates, designers identify which version resonates more effectively with the audience. A/B testing provides data-driven insights, enabling evidence-based design decisions.
Design Research Process
It is a systematic and iterative process that guides researchers in creating user-centered and innovative solutions. Here’s an overview:
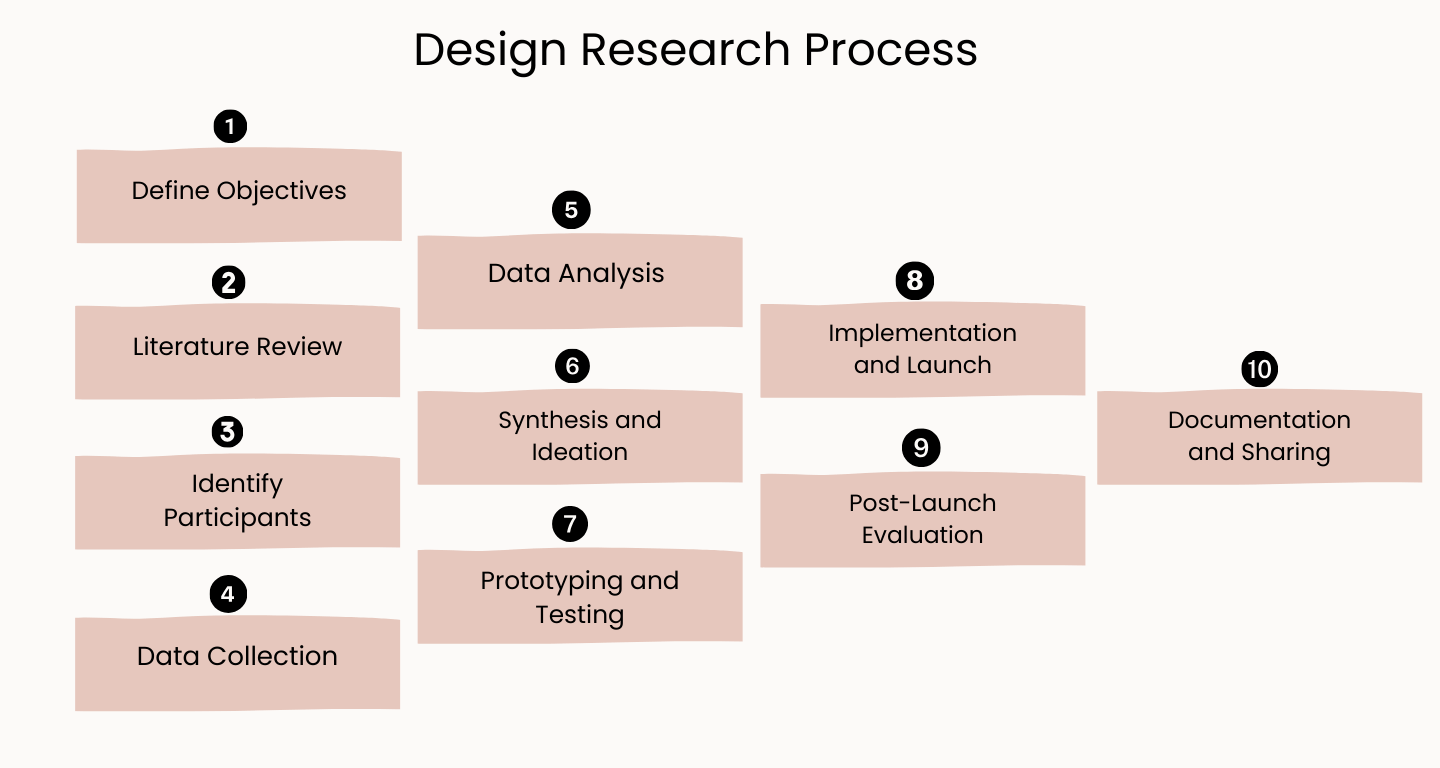
#1 Define Objectives
Begin by clearly defining the research objectives. What do you want to achieve with the research? Establish specific goals, whether it’s understanding user needs, evaluating an existing design, or generating new ideas.
#2 Literature Review
Conduct a literature review to understand existing knowledge and research related to your objectives. This step helps researchers build on existing theories and ensures the study’s relevance and contribution to the field.
#3 Identify Participants
Determine the target audience for your research. Identify user groups, demographics, and characteristics relevant to your objectives. Participants can be current users, potential users, or specific user segments.
#4 Data Collection
Choose appropriate methods for data collection based on your research objectives. Methods can include surveys, interviews, observational studies, or usability testing. Collect both qualitative and quantitative data to gain a comprehensive understanding of user behaviors and preferences.
#5 Data Analysis
Analyze the collected data to identify patterns, themes, and insights. Qualitative data may involve coding and thematic analysis, while quantitative data can be analyzed using statistical methods. Data analysis transforms raw information into actionable insights.
#6 Synthesis and Ideation
Synthesize the findings from the data analysis. Identify key insights and user needs. Use these insights as a foundation for brainstorming and ideation sessions. Collaborate with designers and stakeholders to generate creative solutions based on the research findings.
#7 Prototyping and Testing
Create prototypes or mockups of the proposed solutions. It could be digital interfaces, physical products, or service blueprints. Conduct usability testing with real users to evaluate the prototypes. Gather feedback to refine the designs iteratively.
#8 Implementation and Launch
Once the designs are refined and validated through testing, proceed with implementation. Develop the final product, ensuring it aligns with the user insights and design requirements. Launch the product or service to the target audience.
#9 Post-Launch Evaluation
After the product is launched, continue to gather feedback and conduct post-launch evaluations. Monitor user interactions, collect user feedback, and assess the product’s performance. This feedback loop helps in making continuous improvements and updates based on user experiences.
#10 Documentation and Sharing
Document the entire research process, including objectives, methods, findings, and insights. Share the research findings and design outcomes with stakeholders, team members, and the broader community. Effective communication ensures that everyone involved understands the research outcomes and their implications for the design.
A number of advanced platforms are available to streamline this process. Once you define your objectives, consider using platforms such as SurveySparrow to save time and effort. You can create, collate, analyze, and act all in one place!
Try it out for free today!
14-day free trial • Cancel Anytime • No Credit Card Required • No Strings Attached
Design Research Methodologies
As you saw, the design research process is a detailed and complex process. To facilitate a smooth flow of the same, several methods are employed. Here are a few common ones:
- Surveys & Interviews: Gather user insights systematically.
- Observational Studies: Observe user behavior in real contexts.
- Usability Testing: Evaluate prototypes with real users.
- Card Sorting: Organize information based on user logic.
- Focus Groups: Facilitated discussions to understand opinions.
- Contextual Inquiry: Study users in their natural environments.
Importance Of Design Research
User-Centric Solutions: It ensures products align with user needs, preferences, and behaviors, enhancing user satisfaction.
Risk Mitigation: By understanding user expectations, businesses can identify and address potential issues before they escalate, minimizing risks.
Innovation Driver: Design research fosters creativity, inspiring novel ideas and breakthrough innovations that set products apart in the market.
Cost Efficiency: Addressing user needs early in the design process prevents costly redesigns later, saving both time and resources.
Competitive Edge: Products crafted through design research stand out, creating a competitive advantage in a crowded market.
Enhanced User Experience: Intuitive designs born from research make user interactions seamless, leading to higher customer loyalty and positive reviews.
Long-Term Success: Understanding evolving user preferences ensures products remain relevant and successful in the long run.
Wrap Up!
Let’s end this by sharing how we at SurveySparrow boost productivity by focusing on design research. By conducting an in-depth analysis, we explore preferences regarding survey formats, question types, and user interface elements. Usability testing is employed to identify friction points and gather real-time feedback. This user-centric approach leads to a surge in user satisfaction. And, yes, it is not a one-time event. We keep it as our priority to do continuous and rigorous research to improve and optimize customer satisfaction!
So, if you wish to up your game, go ahead and start today. Again, give SurveySparrow a try before you leave. It’s free!
14-day free trial • Cancel Anytime • No Credit Card Required • No Strings Attached

Create engaging surveys that people actually complete. Try SurveySparrow now!
Kate Williams
Related Articles

Survey & Feedback
Ideal Proxies For Surveys
6 MINUTES
14 April 2022

Survey & Feedback
Top 4 Medical Survey Portals to Make Extra Money
10 MINUTES
3 September 2024

Survey & Feedback
Double-Barreled Questions: Definition, Examples, and How to Avoid Them
12 MINUTES
24 June 2022

Survey & Feedback
How to Create Multilingual Surveys for Global Commercial Real Estate Loans: A Step-by-Step Guide
9 MINUTES
30 January 2026
