Product Testing: Insights, Strategies and Best Practices

Kate Williams
Last Updated: 30 October 2023
10 min read

Have you ever wondered how a product went from a mere idea to a tangible item in your hand? The secret behind this transformation lies in a pivotal step: product testing. It’s more than just a routine. It ensures that what you buy is not just a product but a promise of quality and satisfaction.
So, what is product testing, and why is it so pivotal? In this blog, we will go deep into its core, exploring its importance, benefits, strategies, and best practices.
What is Product Testing?
Product testing is the meticulous art of scrutinizing a product under controlled conditions. During this process, every facet of the product, from its functionality and durability to its safety and user-friendliness, is rigorously examined and evaluated.
Think of it as a litmus test for innovation!
We know how every detail is so crucial in product development. Here, product testing acts as the judge and ensures that the product meets the quality requirements and exceeds the expectations of the end-user.
For instance, imagine you have come up with a groundbreaking idea for a gadget. It promises to revolutionize the way people interact with technology. It’s sleek and intuitive. But how do you know it won’t falter in the hands of its users? This is where testing a product steps in. It’s the phase where your creation faces real-world challenges, ensuring it stands tall amidst varying conditions and user interactions.
Product Testing vs Concept Testing
While they might sound similar, product testing and concept testing have their characteristics. They play distinct roles in the phase where an idea takes the shape of a reliable product.
| Concept Testing | Product Testing | |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Ideas, Reactions | Functionality, User Experience |
| Purpose | Viability Check | Quality Assurance |
| Stage | Initial | Intermediate/Final |
| Feedback | Reactions, Ideas | Practicality, Durability |
| Scope | Narrow | Comprehensive |
| Outcome | Concept Refinement | Product Perfection |
1. Focus
- Concept Testing:(CT) Exploring Ideas, Capturing Reactions
In this phase, it’s all about brainstorming innovative ideas and seeing how people react. We’re checking the pulse of the concept, figuring out if it resonates with potential users.
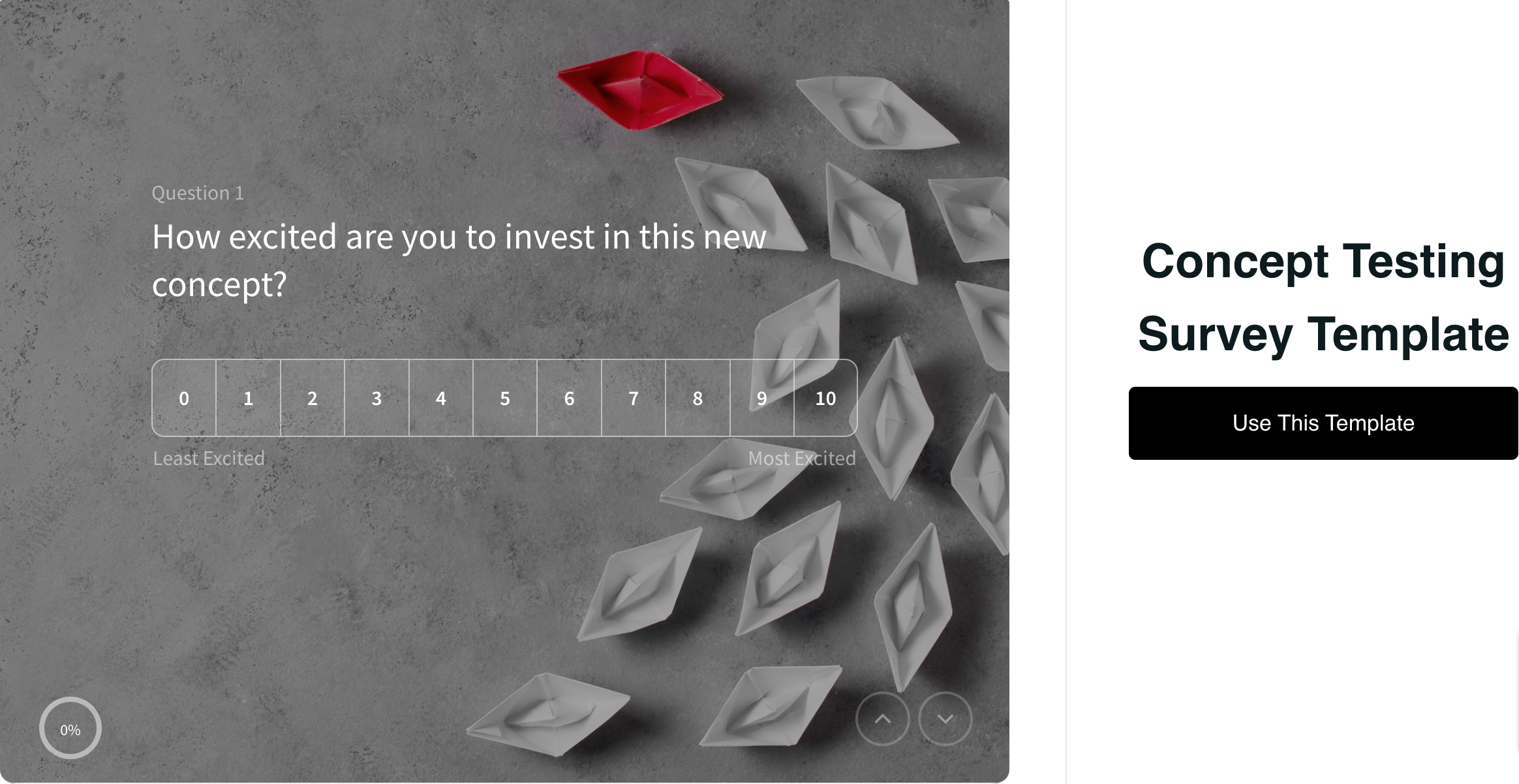
Curious about it? Here’s a concept testing survey template for you to get a clear idea of how it looks.
- Product Testing:(PT) Checking Functionality, User Experience
Product testing dives deeper. It’s about making sure the product not only works but works well for users. We’re keen on seeing how people interact with it, ensuring it’s not just functional but also user-friendly.
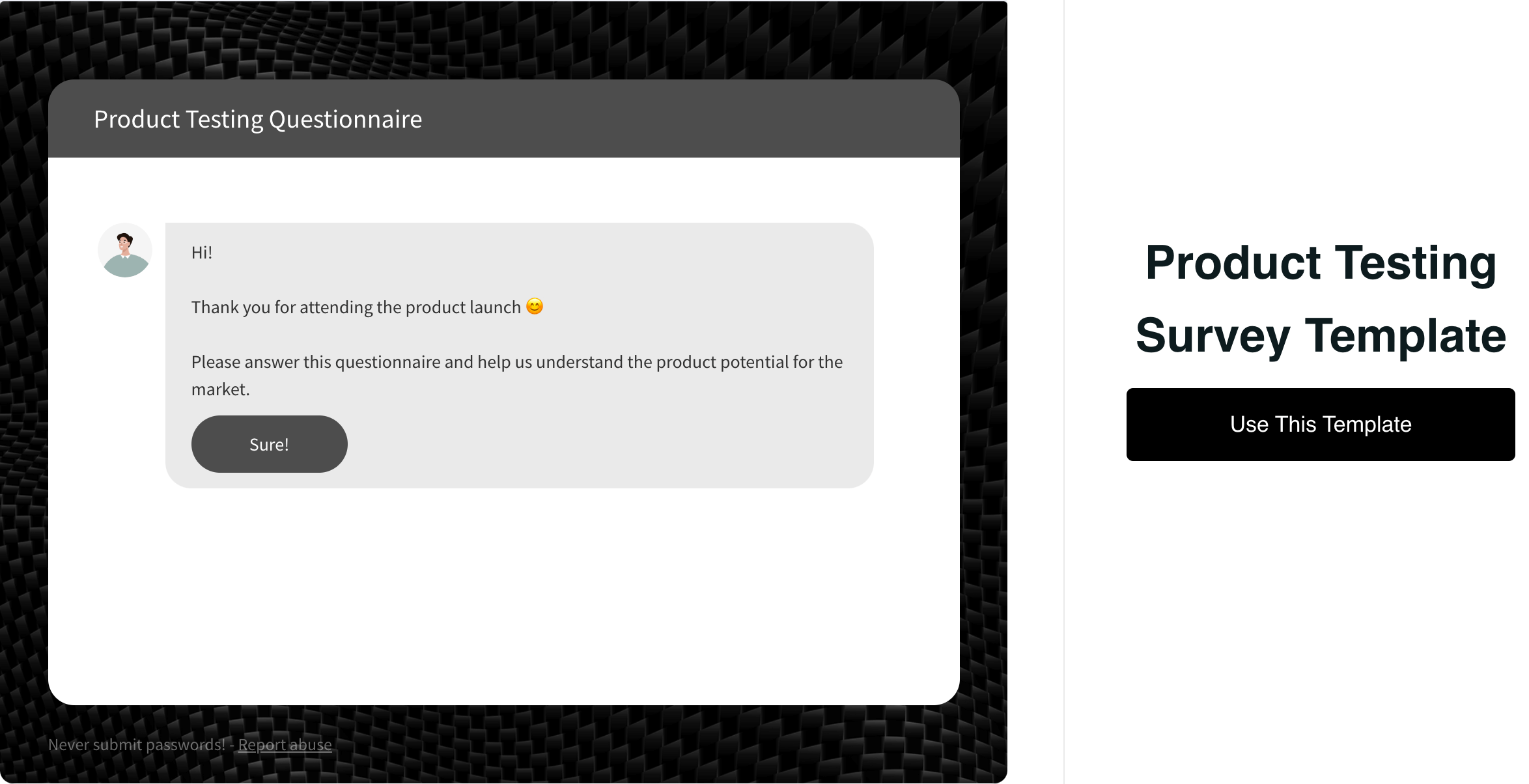
And, this is a product testing survey template:
2. Purpose
CT: Viability Check
Concept testing serves as a viability check, determining whether the initial idea is practical and feasible. It helps in identifying potential challenges and limitations before investing further resources.
PT: Quality Assurance
Product testing focuses on ensuring the product meets quality standards and customer expectations. It acts as a quality assurance measure, identifying and rectifying issues to deliver a reliable and user-friendly product.
3. Stage
CT: Initial
Concept testing occurs in the early stages of product development when ideas are in their infancy. It acts as the preliminary assessment before significant resources are invested in prototype development.
PT: Intermediate/Final
Product testing takes place in the intermediate to final stages of development. It involves evaluating prototypes and near-final products to ensure they are market-ready and meet the desired quality standards.
4. Feedback
CT: Initial Reactions and Bright Ideas
We’re interested in those initial “aha” moments and any brilliant ideas users might have. It helps in understanding user preferences and potential improvements.
PT: Practicality and Sturdiness
Here, it’s all about practicality. Does it make sense in real life? And of course, we’re looking at sturdiness too. Is it durable? Will it stand the test of real-world usage?
4. Scope
CT: Narrow
Concept testing has a narrower scope, concentrating on specific aspects of the idea such as its appeal, relevance, and initial impressions. It aims to answer fundamental questions about the concept’s potential.
PT: Comprehensive
Product testing has a broader scope, encompassing various aspects of the product, including functionality, safety, durability, and customer satisfaction. It offers a comprehensive evaluation of the product’s overall performance.
5. Outcome
CT: Concept Refinement
Concept testing often leads to polishing the initial gem of an idea. We refine and reshape based on feedback, making it shine brighter before moving forward.
PT: Perfecting the Product
Product testing is about perfection. It’s not just about fixing issues; it’s about fine-tuning every detail, ensuring the product is not just good but outstanding.
Importance of Product Testing
Imagine you are excited about the launch of a smartphone in the market. You booked it and are eagerly waiting for it. But what if, upon arrival, it malfunctions and doesn’t meet your expectations? You’ll be disappointed. Right?
This disappointment is precisely why product testing is not just a box to tick. Let’s look at its importance:
1. Ensuring Quality Assurance: It is the gold standard for guaranteeing a product’s flawless performance under diverse conditions, instilling trust in customers.
2. Risk Mitigation: By identifying potential issues before launch, product testing saves businesses money, safeguards reputation, and ensures a seamless user experience, fostering loyalty.
3. Customer Satisfaction: Thoroughly tested products exceed customer expectations, cultivating satisfaction, and brand loyalty among users.
4. Fostering Innovation: It provides valuable insights, fueling innovation by pinpointing areas for enhancement and driving continuous improvement.
5. Regulatory Compliance: Testing ensures products adhere to industry regulations, safeguarding both legal compliance and consumer safety.
6. Building Brand Reputation: Quality-tested products bolster brand credibility. This establishes a strong reputation based on reliability and user satisfaction.
How to Evaluate a Product
With the right approach, it becomes a strategic process. Even better, with the right tools you can streamline the entire process. For instance, you can use the advanced survey tool offered by SurveySparrow. The platform lets you create surveys, share them on multiple platforms, collate data, analyze them, and act upon the insights you gain!
14-day free trial • Cancel Anytime • No Credit Card Required • No Strings Attached
Now, here’s a guide to make things easier:
1. Define Clear Objectives
Determine specific goals for the testing phase. Clearly outline what aspects of the product you want to evaluate, ensuring your objectives are specific, measurable, and achievable.
2. Create Realistic Test Scenarios
Develop practical and real-world scenarios that mimic how users will interact with your product. These scenarios should cover a wide range of situations to comprehensively assess the product’s performance.
3. Gather a Diverse Test Group
Include individuals who represent your target audience. Diversity in your test group ensures varied perspectives and helps identify potential issues from different user viewpoints.
4. Use Reliable Tools and Technologies
Employ cutting-edge testing tools and technologies that offer accurate and reliable results. These tools can range from software for usability testing to specialized equipment for stress and durability tests.
5. Analyze Data and Iterate
Carefully analyze the data collected during testing. Identify patterns, trends, and areas of improvement. Use this data to make necessary iterations to the product, addressing identified issues and enhancing its features.
What you need to keep in mind is that product testing is not a one-time event. It is an iterative process.
Key Metrics in Product Testing
Consider these fundamental metrics when evaluating your product:
- Functionality: Does the product perform its intended functions seamlessly?
- Usability: How user-friendly is the product? Can users navigate it effortlessly?
- Durability: How well does the product withstand wear and tear, ensuring longevity?
- Safety: Is the product safe for use, adhering to industry standards and regulations?
- Performance: How does the product perform under various conditions and stress tests?
What is a Product Lifecycle?
The product lifecycle is the journey a product goes through from its introduction to the market until its withdrawal or discontinuation. This cycle is typically divided into several key stages:
1. Development Phase: Refining Prototypes
During the early stages, product testing refines prototypes. It is similar to when a sculptor chisels away imperfections, ensuring the prototype aligns seamlessly with the envisioned product. By identifying and rectifying issues, it sets the foundation for a robust product.
2. Testing Phase: Ensuring Market Readiness
In the testing phase, products face scrutiny. Product testing identifies and rectifies potential pitfalls before market launch. It acts as a safeguard, ensuring the product is not only functional but also appealing, user-friendly, and durable.
3. Market Phase: Real-Time Feedback for Enhancements
Once in the market, product testing doesn’t stop. It provides real-time feedback from users, offering valuable insights for enhancements. Whether it’s addressing user suggestions or adapting to market trends, this feedback loop keeps the product competitive and relevant.
4. Post-Market Phase: Monitoring Performance
Even after the launch, product testing continues its role. Monitoring the product’s performance in real-world scenarios helps in identifying areas for improvement. Timely updates and improvements based on this ongoing testing ensure the product remains fresh and appealing to users.
Best Practices for Effective Product Testing
To ensure your product testing process is not just comprehensive but also efficient, consider these best practices:
- User-Centric Approach: Prioritize user experience, tailoring tests to match user expectations and behaviors.
- Real-World Simulation: Mimic real-life scenarios to identify potential issues that users might face in their daily interactions with the product.
- Continuous Iteration: Embrace an iterative approach, continuously refining the product based on test results and user feedback.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Foster collaboration between different departments, incorporating diverse perspectives and expertise.
- Compliance and Standards: Adhere to industry regulations and standards, ensuring the product meets legal requirements and safety norms.
Wrap Up!
So, whether you’re a curious inventor or a smart shopper, product testing is what guarantees that what you get is not just good but great. Every efficient app, every durable gadget, and every dependable tool you use has undergone rigorous testing. This is what makes everyday items trustworthy and enjoyable to use.
Care to give our thoroughly tested survey tool a spin? It’s free to try!
Create conversational surveys with SurveySparrow
Get at least 40% completion rates for your surveys
14-Day-Free Trial • Cancel Anytime • No Credit Card Required • Need a Demo?

Kate Williams
Content Marketer at SurveySparrow
You Might Also Like

Turn every feedback into a growth opportunity
14-day free trial • Cancel Anytime • No Credit Card Required • Need a Demo?