VoC
Qualitative Feedback: Complete Guide to Collection, Analysis & Examples
Article written by Kate Williams
Content Marketer at SurveySparrow
14 min read
19 September 2025

60 Seconds Summary:
Qualitative feedback helps you understand the 'WHY' behind your customers buying decisions, even beyond the numbers. This guide unpacks what qualitative feedback is, why it matters, and how to collect and analyze it effectively. You'll learn how open-ended questions, interviews, and user observations can uncover deep insights into emotions, motivations, and experiences. Discover actionable techniques, real-world examples, and how tools like SurveySparrow streamline the process for smarter decision-making and continuous growth.
Some customer insights give you so much more impactful value than the others. The difference lies in the type of feedback you collect. Numbers and ratings show you what is happening while it rarely shows the why behind why customers behave a certain way.
Feedback is something through which businesses or researchers get insights. One crucial type to focus on is qualitative feedback. Rather than some numerical points, this type of feedback captures customer expressions as such. In other words, more nuanced customer feedback.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about qualitative feedback – from definition to collection methods, analysis techniques, and practical applications across industries. Click here, if you want to jump to the template.
So, let’s get started.
What Is Qualitative Feedback?
Qualitative feedback is customer opinions that offer detailed and descriptive information. The type of feedback refers to descriptive, non-numerical information collected from customers, users, or stakeholders that provides insights into their experiences, opinions, motivations, and feelings.
The feedback is primarily based on observations or, in other words, it’s not quantifiable. This type of feedback is mostly used across education, customer service, and management. A common example of qualitative feedback is shown below.
Standard Feedback: “The product did the job 👍.”
Qualitative Feedback: “The functionality of the product was very good, especially the conversational interface and AI surveys. There’s a learning curve, but the support team was at every step helping us.”
The qualitative version provides:
Specific product features that worked well (conversational interface, AI surveys)
Challenges encountered (learning curve)
Service experience (helpful support team)
Emotional context behind the experience
As you can see, the feedback includes personal experience and views – rich and detailed.
What Makes Good Qualitative Feedback?
Not all descriptive feedback is equally valuable. High-quality qualitative feedback typically includes:

Specificity: Details about particular features, interactions, or experiences
Context: Situation or circumstances in which the experience occurred
Emotional content: How the experience made the person feel
Reasoning: Why certain aspects were positive or negative
Suggestions: Ideas for improvement based on the experience
Types of Qualitative Feedback
Qualitative feedback comes in several forms, each offering unique insights:
Descriptive comments - Detailed explanations of experiences
Narrative feedback - Stories about interactions with products/services
Visual feedback - Images, videos, or screen recordings showing experiences
Audio feedback - Verbal descriptions through voice recordings
Observational feedback - Notes from watching users interact with products
Why Is Qualitative Feedback Important?
There are many reasons why qualitative feedback is important. You might already know some, but here are the key reasons why –
- With the insights being rich and descriptive, it can help improve or enhance your product or service.
- The feedback will be focused, making it more relevant and reliable.
- It can help you understand the ‘WHY‘ behind customer reviews and get a wider picture of customer satisfaction.
- In the education context, this feedback type can be highly helpful in understanding complex concepts and improving skills – both students and teachers.
- You can identify hidden patterns and trends in advance.
These benefits are a few (but the most crucial ones) that are common across niches. Read n to learn more about qualitative feedback.

Undertsand the “Why” Behind Customer Opinions With SurveySparrow!
A personalized walkthrough by our experts. No strings attached!
Key Applications of Qualitative Feedback
We have already discussed three areas in which qualitative feedback is used. Here, we will be listing the industries that require qualitative feedback. Let’s have a look at them.
- Education – For developing and improving the skills of both teachers and students.
- Business – For managers to provide constructive feedback on employee behavior, achievements, and areas of growth.
- Research: To collect and discuss the implications of research findings and theories in depth.
- Healthcare: For doctors and nurses to discuss patient care, improve practices, and patient outcomes.
Now that you have a basic idea of qualitative feedback, let’s discuss how you can collect it.
Qualitative vs Quantitative Feedback: What’s the Difference?

Both quantitative and qualitative feedback is essential to get a complete view of customer experience. Since you already know what qualitative feedback is, let’s discuss the latter.
Quantitative feedback is numerical and focuses on measuring opinions or other variables. They are structured and often use scales, checkboxes, or numeric inputs to gather feedback. A good example is NPS® surveys. The NPS® score is numerical and clearly gives you an idea of customer loyalty.
The following is a quick read for you to acknowledge the difference between the concepts.
| Aspect | Qualitative Feedback | Quantitative Feedback |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Descriptive and detailed, focuses on understanding behaviors, experiences, and perceptions. | Numerical and measurable, focuses on quantifying opinions, behaviors, or variables. |
| Nature of Data | Non-numerical, text-based (words, images). | Numerical (numbers, statistics). |
| Collection Methods | Interviews, focus groups, observations, open-ended surveys, and ethnographic research. | Structured surveys, polls, experiments, and closed-ended questions. |
| Data Analysis | Coding, thematic analysis, content analysis, narrative analysis. | Statistical analysis, including descriptive and inferential statistics. |
| Output | Detailed descriptions, direct quotations, and thematic summaries. | Statistical figures, charts, graphs, percentages. |
| Interpretation | Provides depth and detail and explores how and why phenomena occur. | Offers breadth, tests hypotheses, and generalizes findings to larger populations. |
| Applications | Exploring complex issues, developing hypotheses, user experience research, and initial research phases. | Confirming hypotheses, estimating outcomes, large-scale studies, and generalization. |
| Advantages | Depth of insight uncovers trends in thought and opinions and provides context. | Quick analysis, large sample sizes, objective and generalizable results. |
| Limitations | It is less easy to generalize, time-consuming and has the potential for researcher bias. | May overlook reasons behind trends and less detail on individual experiences. |
What are Some Qualitative Feedback Examples
The following are some examples of qualitative feedback. We are providing how the feedback would look on key industries. Hopefully, this will help you identify qualitative feedback instantly.
In customer service – customer review
“The support team was very attentive and knowledgeable. They were able to pinpoint my issues quickly and offer tips to resolve them. Altogether, I had a great experience.”
In healthcare – patient feedback
“The physical therapy sessions have been helpful, but I feel they are rushing through the process. I’m also unable to discuss discomfort and pain level with my trainer during the sessions.”
In the workplace – performance review
“You have shown great initiative and leadership qualities throughout the year. And the way you have managed the clients, especially during the onboarding, has been impressive. Moving forward, integrating more data-driven strategies could further enhance your decision-making process.”
In product development – user testing feedback
“The interface of the new features is visually appealing. However, I found the exporting function to be confusing. The option is currently hidden from the users under another menu. We should make it more accessible for the users.”
In hospitality – a guest review of a hotel
“The room was very clean, and the ambiance was equally great. There was an issue with the heater, so we weren’t able to use hot water. The food was great, with a lot of options, but the room service could be improved.”
Let’s see how you can collect these kinds of feedback.

Undertsand the “Why” Behind Customer Opinions With SurveySparrow!
A personalized walkthrough by our experts. No strings attached!
How to Collect Qualitative Feedback?
Qualitative feedback collection is a tricky one. There are several methods to go about it, but before jumping into them – define your goal. You must have a clear idea of what you are trying to achieve with the feedback.
- Are you trying to improve your product?
- Do you want to evaluate your asset condition?
- Is it the user experience you want to measure?
Ask yourself what you want to achieve and define the goal first. Once you have done that, choose any of the following methods for collecting qualitative feedback.

Method 1 – Open-ended Surveys
The most common and best way to collect qualitative feedback is through surveys. With the right survey tool by your side, you can reach out to a global audience and collect feedback efficiently. Not to mention the multiple channels you can collect from.
By asking open-ended survey questions, respondents can express their feelings without any constraints. You can then analyze them to understand the following (but are not limited to) –
- What prompted them to give the feedback
- The customer sentiment behind the feedback
- The reasons behind their emotions
- The areas you need to work on
To give you a better idea of how effective surveys can be, refer to the qualitative feedback template below. The template is free to use (upon sign-up). So please, feel free to use it.
Qualitative Feedback Survey Template
Use This TemplateMethod 2 – Interviews
Interviews are basically a limited and time-consuming version of surveys, albeit an effective one. It allows for in-depth discussions and can adapted based on the respondent’s answers.
NOTE:
This is also possible in surveys. However, you have to choose the right tool. SurveySparrow offers skip and conditional logic to make the surveys smart and dynamic. Try out SurveySparrow for free and see the difference for yourself.
Now, back to interviews. you can conduct interviews in two ways –
- Structured
- Unstructured
- Semi-structured
In structured interviews, there will be a set of predefined questions to ask the respondents. This is to ensure uniformity across interviews. A limitation here is the depth of response.
In the case of unstructured interviews, the questions will be open-ended. In addition, the interviewee will guide the entire discussion to cover all topics and uncover deeper insights.
Semi-structured interviews are a mix of both. There will be a set of predefined questions, but the interviewee can also drive the discussion to make it more insightful.
Method 3 – Focus Groups
If you are someone who has done market research, then you will be familiar with them. These are practically a group of individuals handpicked to discuss specific topics (or products). Following this method can be useful in exploring a wide range of perspectives.
While creating a focus group, ensure a safe environment where the participants can express themselves without constraints. As a result, you can see more interaction between them, leading to new insights and ideas.
The moderator you hire should also be skilled to drive discussions efficiently. The discussion should not wander off-topic and should cover every aspect of the topic. If you are interested, you can follow the link where we discuss focus groups in detail and how to create one.
The methods we discussed are the best ways for qualitative feedback collection. Though there are other methods, they usually bring in a mix of both qualitative and quantitative feedback. Now, let’s see how to analyze the feedback.
How to Do Qualitative Feedback Analysis?
Once you have collected the feedback, it’s time to analyze it. However, qualitative feedback analysis is an intricate process. This is the case, especially because of the volume and nature of data that need to be analyzed.
Don’t worry – here’s a structured approach to make qualitative feedback analysis easy.

Step 1 – Data Preparation
You can’t just analyze the collected data just like that. No. You need to organize and prepare them first.
Check for audio or video feedback. If there is, then convert them into text. Remember to check for accuracy while converting the data. The level of data accuracy will define the integrity of the data.
Categorize the feedback according to topics or questions and remove any irrelevant or redundant data. Move on to the next step when you have completed these.
Step 2 – Code Your Data
Coding here means to categorize and tag the data. It usually involves identifying data segments and applying labels (code) to them. These codes can be descriptive, inferential, or thematic. The coding is done in three stages. They are as follows –
- Open coding – Start with open coding by labeling data with as many codes as seems appropriate. This stage aims to describe the content.
- Axial coding – Here, organize these codes into categories based on their relationships. Doing so helps identify the connections between different parts of the data.
- Selective coding – At the final stage, identify one or more central themes that hold your analysis together. This involves integration and refining the categories into major themes.
This process is like piecing together a puzzle in an orderly fashion. Through coding (labeling), you can clearly differentiate feedback that discusses specific topics.
Step 3 – Develop Themes
Themes are basically a way to capture the essence of a larger chunk of data. For instance, we have categorized feedback into usability, payment portal, and product efficiency. However, the underlying focus of this qualitative feedback is customer experience. That’s what themes do.
Thematic mapping can be helpful. The visual representations can provide a crystal clear relation between feedback. Thus, it makes analysis easier.
Step 4 – Interpret Data
Once the themes are set in place, it is time to interpret the feedback data. You need to check the data in relation to your initial questions or objectives. Ask yourself – how do the themes fit into the larger picture of your feedback goals? This will help you understand the context of the qualitative feedback.
Step 5 – Report the Findings
Prepare a concise report to summarize the findings. Make sure to include the following while creating the report so that it covers everything.
- Use direct quotes from participants to illustrate key points.
- Clearly explain how you derived the themes and what they represent.
- Point out your findings and how they can help with your business growth.
Once the report is ready, share it with the teams and stakeholders. Go through the report insights and take appropriate actions to grow your business.
PRO TIP💡:
Start with negative feedback and prioritize its resolution. Dissatisfied customers are more prone to sharing their experience (word of mouth) than satisfied ones. Take prompt action to resolve their issue and communicate the same to them.
This shows you are committed to providing better customer experience and value them.
Collect Qualitative Feedback With SurveySparrow
As you may have understood, qualitative feedback analysis is a complex and time-consuming process. But with SurveySparrow, it isn’t.
For qualitative feedback collection, it offers a conversational survey interface. With the surveys being interactive and engaging, you can expect a 40% more response rate. And by allowing you to share surveys at key touchpoints, you can get reliable and honest feedback.
The user-friendliness and interactivity of the surveys are very evident from the template given below.
Qualitative Feedback Survey Template
Use This TemplateYou can collect feedback from different channels.
The platform allows you to share surveys through 12+ channels, including WhatsApp, SMS, and QR codes. Its ticket management software can help you quickly reach out to customers who have provided negative feedback. Therefore, it will be easier for you to communicate with them when the issues are resolved.
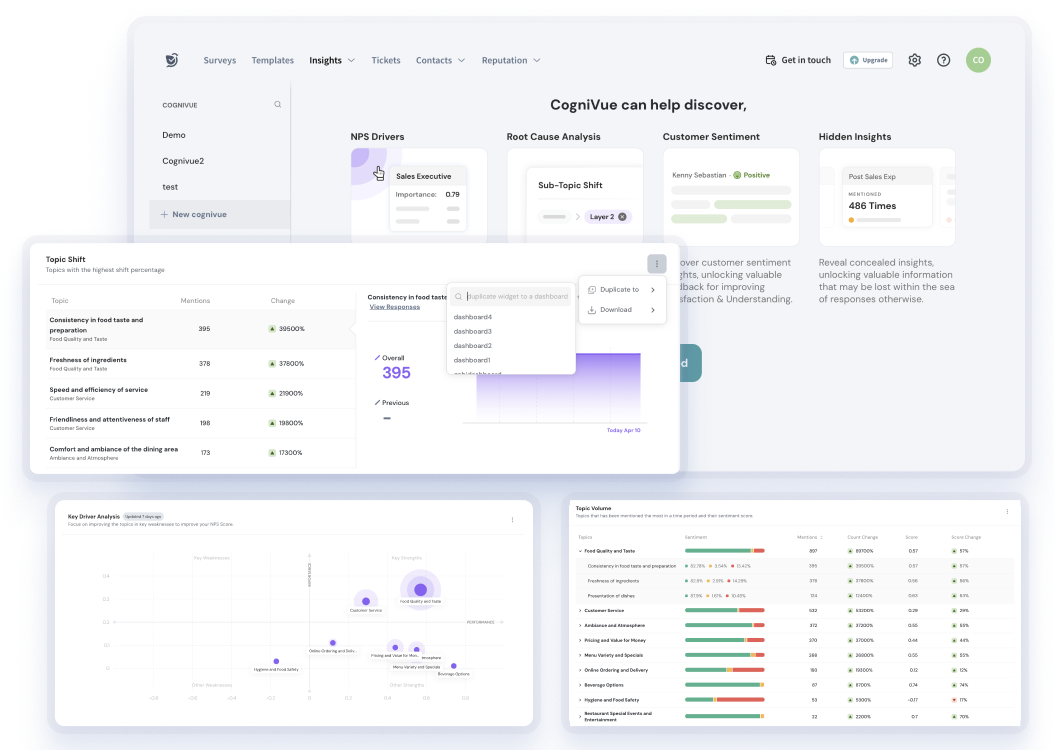
As for the analysis, SurveySparrow offers CogniVue.
It’s an advanced analytics feature that offers you the following insights from feedback analysis.
- Sentiment score
- The most discussed topics in the feedback
- The customer sentiments behind the feedback
- Key driver analysis
- The ‘What’ and ‘Why’ behind customer feedback
Unlike other online survey tools, through this feature, SurveySparrow allows for the collection and analysis of customer feedback from online review platforms. This you will get a comprehensive view of how customers perceive your brand.

Use SurveySparrow for Qualitative Feedback Collection and Analysis!
A personalized walkthrough by our experts. No strings attached!

Turn feedback into growth. Try SurveySparrow’s VoC platform free today!
Kate Williams
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
It is the descriptive feedback that provides insight into student's learning experience. The feedback mostly focus on understanding their thoughts, feelings, and learning process.
Qualitative user feedback is descriptive and subjective, offering insights into user experience. At the same time, quantitative user feedback is numerical and measures user satisfaction through metrics like ratings and scores.
The best way to collect qualitative feedback is to use open-ended surveys, focus groups, and interviews.
The descriptive feedback can provide insight into customer preferences pain point and emotions. Thus it enables you to make personalized improvements that enhance overall satisfaction.
The best method till date is online surveys with open-ended questions. It's faster and cheaper and can reach out to a larger number of audiences.
Related Articles

VoC
What Is Customer Intelligence (CI)? & Why It Is Important
14 MINUTES
27 October 2021

VoC
Launch Your Voice of Customer Program in 30 Minutes Flat!
10 MINUTES
29 June 2018

VoC
User Feedback: Definition, Importance and How to Collect it
13 MINUTES
10 May 2024

VoC
15 Voice of Customer Methodologies to Unleash the Power of Feedback
11 MINUTES
23 June 2023
